Discretionary Benefits
What are discretionary benefits?
Discretionary benefits refer to the range of voluntary benefits that employers choose to offer their employees beyond what is legally required. These benefits encompass various programs and services designed to enhance the overall compensation package provided to employees, contributing to their financial security, health, and wellbeing.
Unlike mandatory or statutory benefits, which are required by law (like social security, unemployment insurance, or workers’ compensation), discretionary benefits are optional and often tailored to meet employees’ specific needs and the organization’s strategic goals.
Examples of discretionary benefits
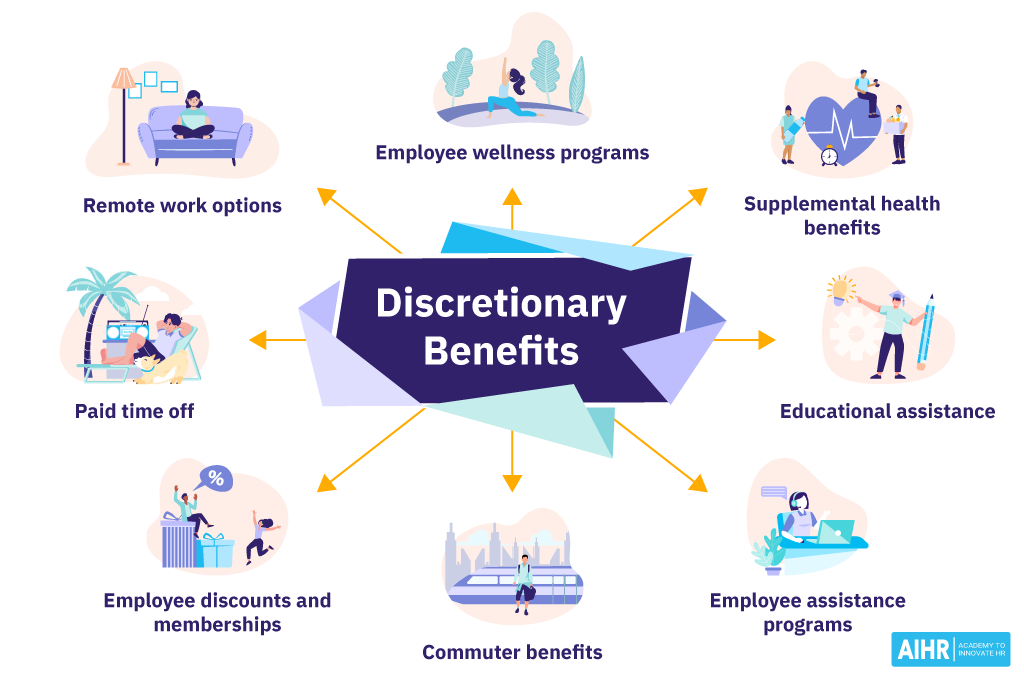
Here’s a look at some common types of discretionary benefits that employers can offer:
- Paid time off: This includes vacations, personal days, and sometimes sick leave, allowing employees to take time off from work while still receiving pay. Many countries have statutory paid time off, but this is not the case in the U.S., where it is offered at the discretion of the employer.
- Remote work options: With the increasing demand for work-life balance, offering flexibility to work from home or other locations can significantly benefit employees.
- Employee wellness programs: These programs may encompass gym memberships, stress management courses, and other initiatives to maintain or improve employee health.
- Supplemental health benefits: Beyond basic coverage, companies might offer premium health insurance plans, including dental, vision, and mental health services, which are more comprehensive than the legal requirements.
- Educational assistance: Programs offering tuition reimbursement or funding for professional development courses.
- Employee assistance programs: These programs provide confidential counseling and support for issues like stress, substance abuse, and personal problems.
- Commuter benefits: This includes assistance with commuting costs, such as transit passes, parking allowances, or shuttle services.
- Employee discounts and memberships: These could include discounts on company products or services, free meals, access to exclusive events, etc.
Legally required vs. discretionary benefits
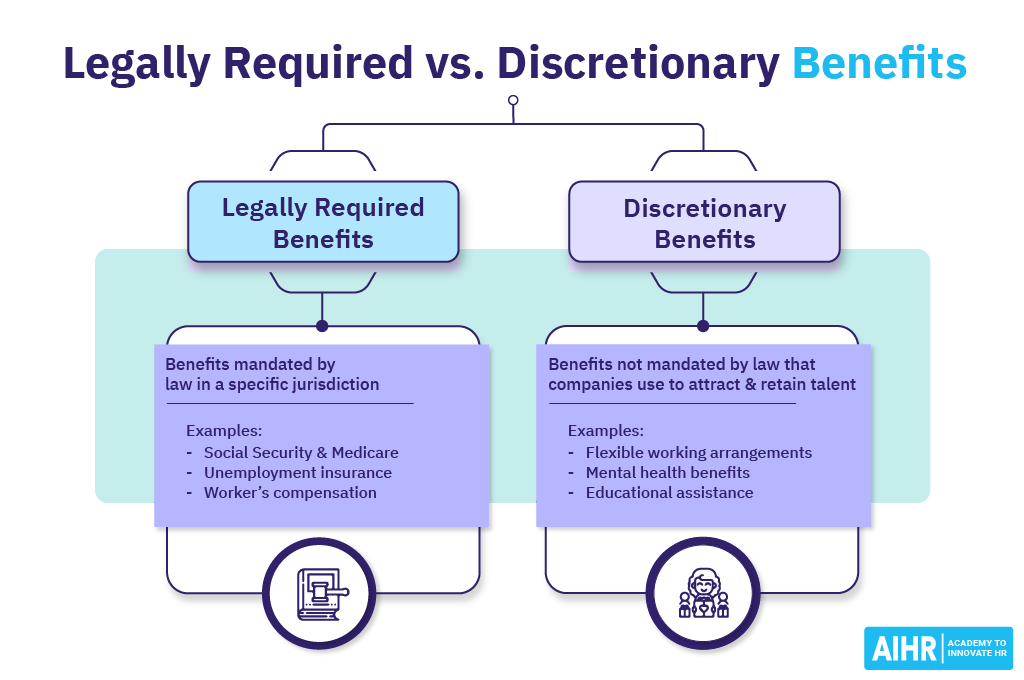
Both legally required and discretionary benefits are crucial for the total compensation package offered to employees. Still, they differ significantly in their nature and the degree of choice employers have in offering them:
Definition
Benefits that employers are required by law to provide to their employees.
Benefits that employers voluntarily choose to offer their employees.
Purpose
To guarantee a minimum level of protection for workers in areas such as health, income, and safety.
To attract, retain, and motivate employees beyond the basic legal requirements.
Examples
– Social Security
– Medicare
– Unemployment insurance
– Workers’ compensation.
– Paid time off (vacations, personal days)
– Flexible work arrangements
– Tuition assistance
– Life and disability insurance.
Regulation
Governed by federal and state laws. Non-compliance can result in penalties.
Not mandated by law, but if offered, may be subject to certain regulations (e.g., ERISA for retirement plans).
Cost to the employer
Costs are largely fixed and mandated by law.
Costs vary based on the scope and generosity of the benefits package offered.
Pros and cons of discretionary benefits
Advantages
- Creates a positive work environment: Benefits such as recognition programs, professional development opportunities, and team-building activities can contribute to a positive work culture.
- Attracts high-quality candidates: Offering a comprehensive benefits package that includes these benefits can make a company more attractive to potential employees.
- Flexibility and responsiveness to employee needs: By offering a wide range of discretionary benefits and allowing employees to choose the ones that are most valuable to them, employers can effectively support their employees’ individual needs and lifestyles.
- Increased productivity: Benefits that support employees’ physical and mental health, such as gym memberships, wellness programs, or flexible working arrangements, can lead to employees being happier, healthier, more engaged, and more productive in their work.
Disadvantages
- Cost implications: The most significant disadvantage is the cost of providing discretionary benefits. Small businesses or startups, in particular, may find it challenging to afford extensive benefits packages, particulary when competing with larger corporations with more resources.
- Complexity in administration: Administering a comprehensive benefits package can be complex and time-consuming. This complexity can increase administrative costs and require additional HR resources.
- Dependency on benefits: Employees may become overly dependent on certain discretionary benefits, which can create issues if the company needs to reduce or eliminate these benefits due to financial constraints.
Determining which discretionary benefits to offer
The best way to determine which discretionary benefits to include in your package should be guided by the needs and interests of your employees. Consider these strategies to direct your decision:
- Assess employee needs and preferences by conducting surveys or focus groups to understand what benefits they value the most.
- Analyze workforce demographics, as different demographic groups may have distinct benefit preferences.
- Benchmark against competitors by looking into what similar organizations in your industry are offering.
- Consider your company’s budget and resources, balancing employees’ desires with your business’s financial realities.
- Monitor the effectiveness of current benefits and adjust based on feedback.
By implementing these procedures, you can develop a strategic approach to offering discretionary benefits, ensuring both the satisfaction of the workforce and the financial health and competitiveness of the company.
HR tip
To maximize your discretionary benefits program’s impact, effectively communicate its details to employees, regularly update it based on feedback, and adopt a flexible platform. This approach enhances benefit relevance, meets individual needs, and ensures the offerings remain valued.
FAQ
Discretionary benefits are crucial because they go beyond basic compensation to enhance employee satisfaction and loyalty. Offering such benefits demonstrates an employer’s commitment to the wellbeing and development of its employees, leading to a positive workplace culture, improved productivity, and a reputation as a preferred employer.
Discretionary benefits are crucial for strategic compensation as they allow employers to tailor their offerings to meet their workforce’s specific needs and preferences. By carefully selecting and managing these benefits, employers can create a compelling employment proposition that aligns with their strategic objectives and fosters a motivated, productive workforce.