Voluntary Benefits
What are voluntary benefits?
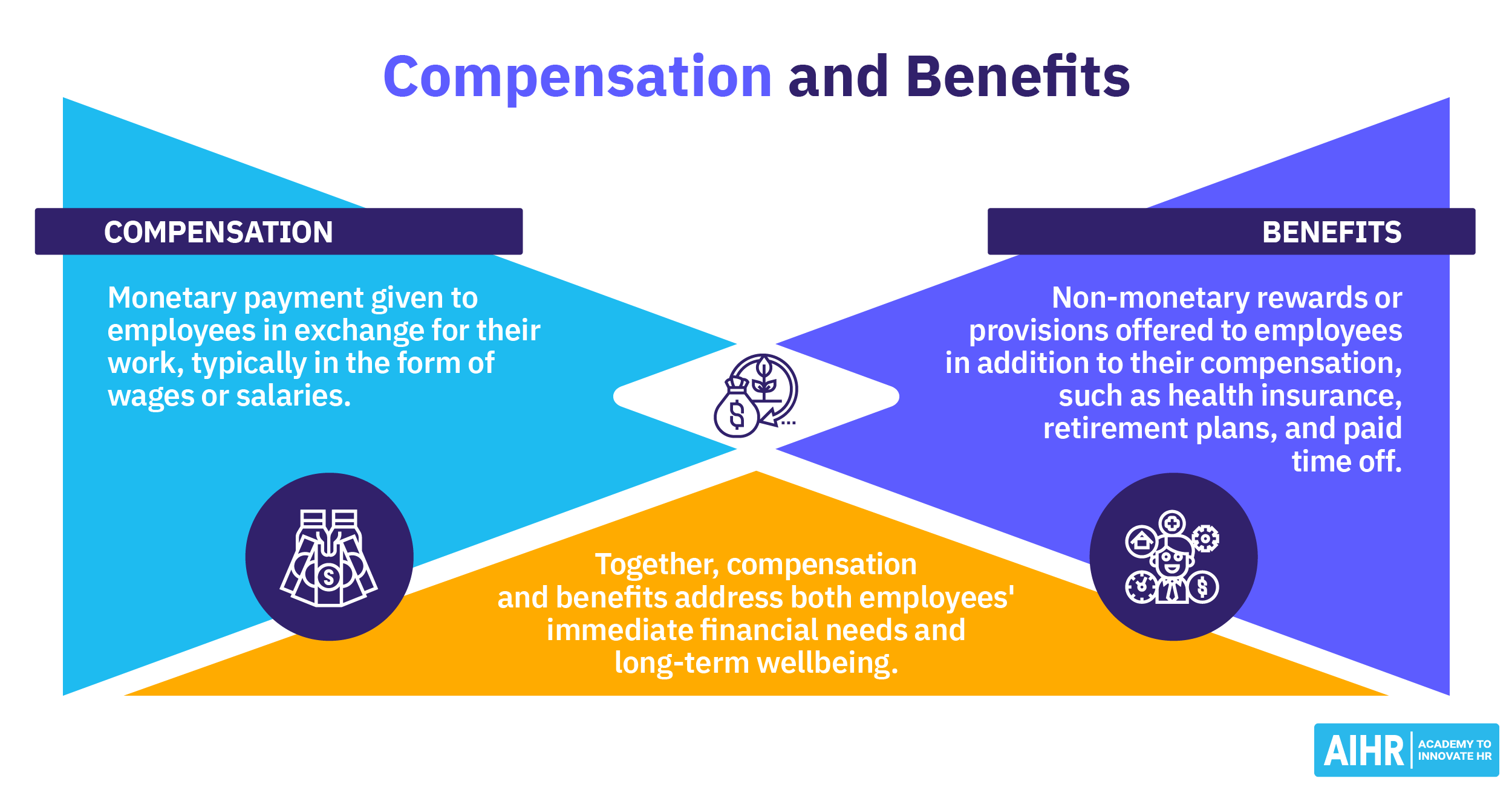
Voluntary benefits are benefits the employee opts into and may pay a portion of the cost. Voluntary benefits are best understood in their contrast to employment benefits. An employment benefit is part of an employee’s contractual compensation; they are automatically provided, and the cost is part of an employee’s pay.
On the other hand, employee voluntary benefits are benefits the employer makes available, and the employee may voluntarily participate in. The cost of voluntary benefits can be complimentary or discounted, paid by the employee, or deducted from their paycheck after opt-in. Many voluntary benefits are pitched as workplace perks that employees may choose to access.
Voluntary benefits examples
There are several different types of employee benefits that each employer should consider when putting together their voluntary benefits package:
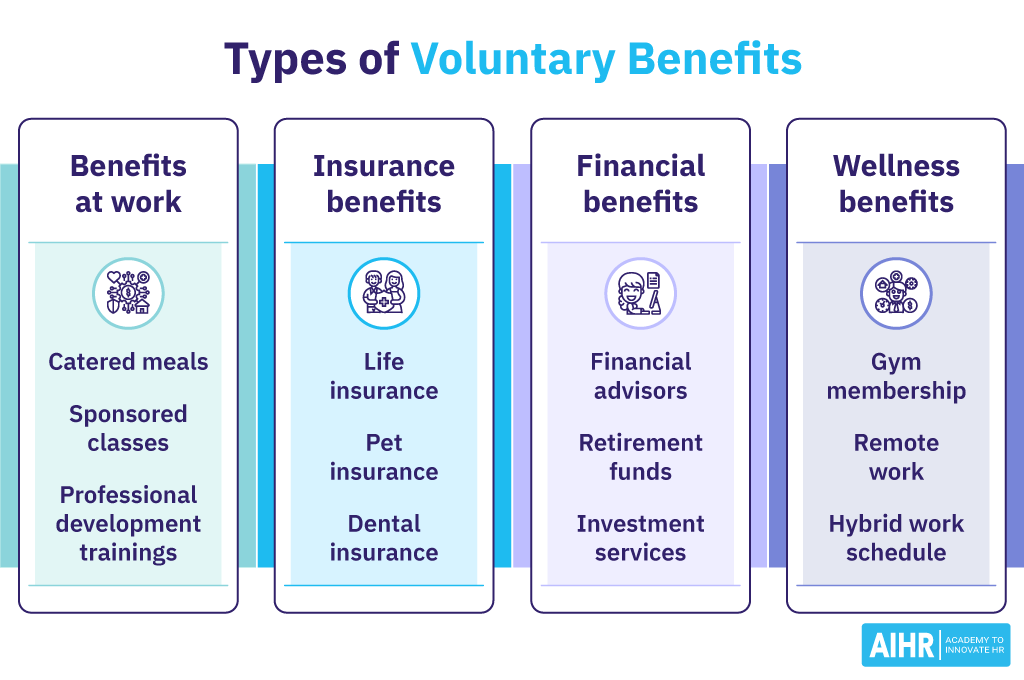
1. Voluntary benefits at work
Workplace voluntary benefits can include catered meals, an office gym, sponsored classes, or professional development training that is available when an employee is at work. It becomes a voluntary benefit at work when the benefit is available to the employee during their working hours or when they are on the premises.
2. Insurance
Insurance is often offered as a voluntary employee benefit. Employers may offer health insurance as a standard benefit, but employees can personalize their insurance profile by opting in to other sponsored types of insurance for an additional cost.
Examples of voluntary insurance benefits include life insurance, pet insurance, critical illness insurance, and other specialized insurance types that are more affordable through the employer than if bought separately.
3. Healthcare
Healthcare voluntary benefits allow employees to tailor their health coverage to their needs. For example, leaving vision insurance as a voluntary benefit provides savings for employees who do not need vision coverage while still covering employees who do. Other types of healthcare voluntary benefits include dental insurance or access to physical therapists.
HR tip
Look for benefits that appeal to the largest number of people in your organization. Keep in mind inclusivity regarding physical access, food allergies, and schedule restrictions so that employee voluntary benefits provide as much effective benefit as possible to your entire staff.
4. Financial
Financial wellness has become a new focus in workplace benefits, and the best way to offer this is through employee voluntary benefits. Examples of financial voluntary benefits include financial advisors, savings programs, managed retirement funds, and access to managed investment services.
5. Wellness
Wellness voluntary benefits are often offered as voluntary benefits so that employees can choose their wellness path. Wellness benefits include gym memberships, meal plans, remote work, hybrid work schedules, and many unique programs that may be available through an employer.
6. Other voluntary benefits
Voluntary benefits can include a wide range of perks that employees can choose to opt into. In addition to the listed categories, employees might join company sports teams, sign up for events and trips, get frequent flyer miles for their travel, participate in contests, or participate in many other unique and beneficial programs an employer might offer.
How to determine which employee voluntary benefits to offer
Many of the most successful brands put together a suite of voluntary benefits that fall into several categories. These categories generally include Health, Financial, Career, and Lifestyle/Wellness. A voluntary benefits program covering all of these bases can also provide for employees with different lifestyles and priorities.
The best way to determine which voluntary benefits to include in your package should be based on the needs and interests of your employees. Consider these strategies to direct your decision:
- Conduct employee surveys to gauge employees’ preferences and needs
- Analyze demographics
- Benchmark competitors
- Assess the financial feasibility of offering specific benefits
- Keep track of benefit utilization and adjust offerings based on feedback and trends
Through these metrics, you can discover which benefits are most desired, most used, and most likely to be appreciated in the future by your staff.
FAQs
A static benefits package is not as flexible as voluntary benefits. A voluntary benefits program can help employees build the lifestyles they desire, even though each person is unique while optimizing the value they receive from their compensation and benefits packages.
They can be. If an employee’s paycheck is used to cover their participation, they can enjoy the cost pre-tax. This is because the employee has consented to alter their compensation in trade for the voluntary benefits.
The most common voluntary employee benefit is additional insurance. Employees often seek to increase their coverage to suit their personal needs with a discount through their employer.
A mandated benefit is a benefit employers must provide by law. For example, unemployment insurance, paid sick leave, and worker’s compensation insurance are mandatory. Voluntary benefits are benefits an employee can take or leave based on their own preference.
Group benefits are offered to all business employees simultaneously, providing the employer and employees with a bulk discount. Voluntary benefits are opt-in for each individual employee.