On-Demand Pay
What is on-demand pay?
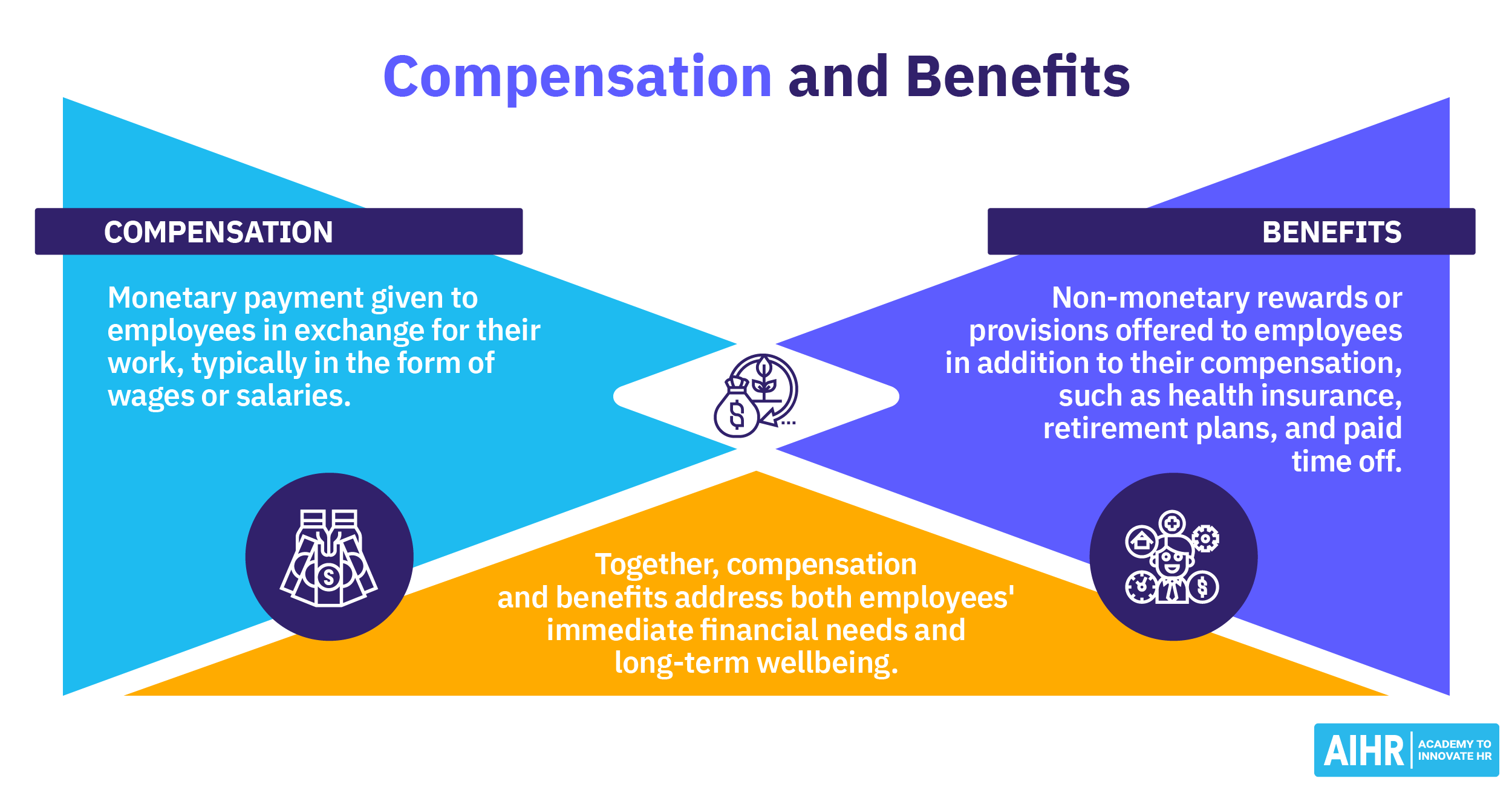
On-demand pay is the ability to request earned pay before a designated pay period. It allows employees to request any pay they have already accrued through work hours, bonuses, and commissions without waiting until their next payday. Most of the time, on-demand pay is provided through an automated platform, so specific approval is not necessary if the service is provided.
On-demand pay allows employees to access their funds and cover expenses on time before payday rolls around. Many consider on-demand pay to be an employee perk and one more way employers can offer flexibility in the employment structure.
How does on-demand pay work?
On-demand pay provides employees early access to their next paycheck. On-demand payroll systems are often automated. Employees are able to log into their financial accounts with the company and review what they have earned. This system works in real time and calculates how much an employee has earned on any given day after tax deductions.
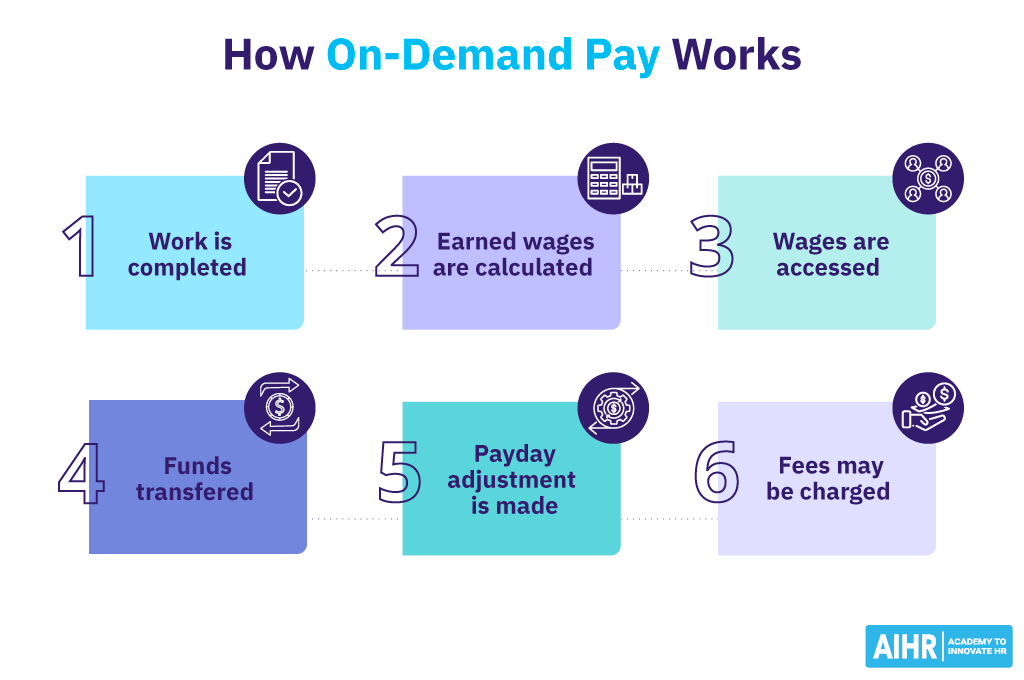
Here’s a basic outline of how it works:
- Work completion: The employee completes their work as usual.
- Earned wage calculation: The on-demand pay service calculates the employee’s wages for the hours they’ve worked so far in the pay cycle. This calculation is typically done in real time or at the end of each workday.
- Wage access: The employee can then request to withdraw a portion of these earned wages before the scheduled payday.
- Fund transfer: The requested funds are transferred to the employee’s bank account or a payment card, depending on the service used and the options available.
- Payday adjustment: On the regular payday, the employee receives the remainder of their wages minus the amount they’ve already withdrawn through the on-demand pay service.
- Fees: Some on-demand pay providers may charge a small fee for each withdrawal, while others offer the service for free. The cost structure depends on the provider.
Advantages and disadvantages of on-demand pay
Advantages
Offering on-demand pay to employees has both its pros and cons:
- Improved employee retention: On-demand pay provides employees financial flexibility and could help reduce financial stress, which can have a positive impact in employee retention.
- Competitive edge in recruitment: Offering on-demand pay can give employers a competitive edge in recruiting, as it’s an attractive benefit for potential employees.
- Increased productivity: Financial stress can negatively impact productivity. Employers can help ease this stress by offering on-demand pay, potentially increasing productivity.
- Reduced absenteeism: Employees facing financial difficulties are less likely to miss work if they have access to their wages when needed.
- Positive employer branding: Offering on-demand pay can enhance the employer’s brand image as being caring and employee-centric.
Disadvantages
Of course, there are also downsides to decoupling pay from traditional payroll cycles.
- Administrative complexity: Implementing and managing an on-demand pay system can add complexity to payroll administration.
- Cost: Depending on the service provider, there may be costs associated with providing on-demand pay.
- Potential for misuse: If not used responsibly by employees, on-demand pay could lead to a cycle of reliance on early wage access, leading to financial instability.
- Regulatory uncertainty: The regulations around on-demand pay are still evolving, which could potentially expose employers to legal risks.
On-demand pay providers
On-demand pay is rarely offered directly by the employer. Instead, on-demand pay companies or pay-on-demand apps act as payroll partners to provide advances on earned income.
| On-demand pay provider | Description |
|---|---|
| DailyPay | DailyPay allows employees to access their earned but unpaid wages on a daily basis. It integrates with companies’ payroll systems and is known for its user-friendly interface and flexibility. |
| Rapid | Provides employees with a PayCard, through which they can access on-demand accrued pay if requested through the Rapid mobile app. |
| Paylocity | Paylocity displays accrued wages in a desktop and mobile app and pre-fund transfers for on-demand pay requests. |
| Clair | Clair is both a payroll and time & attendance system. It offers wage advancements sent to a Clair Spending Account, acting as a job-linked banking system. |
| Square | Square Team App or Square Point of Sale sends a daily hours & earnings email to employees, who can then request up to 50% of their pay on-demand sent to a CashApp or Debit account. Requires the use of Square Timecards. |
| Workday | Payroll management software with multi-regional support. Offers on-demand pay as one of many features. |
How HR can implement on-demand pay
HR must carefully implement on-demand pay to ensure that wages are always accurately calculated and that your chosen on-demand pay provider is a good fit for your company and workforce.
Here are a few tips for HR regarding on-demand pay implementation.
1. Understand the needs of your workforce
Before implementing on-demand pay, conduct surveys or interviews to understand your workforce’s financial needs and preferences. This will help tailor the on-demand pay program to meet the specific requirements of your employees.
2. Choose the right provider
Each on-demand provider works differently. For example, Rapid and Clair both release funds to an internal account rather than the employee’s checking account. Square can only provide 50% of earnings, and Workday is a comprehensive payroll system. Choosing the right provider ensures that you integrate useful software and provide funds in a way that works for your team.
3. Ensure legal and regulatory compliance
Local labor laws may influence how and when payment is distributed. Always check legal and regulatory compliance before implementing a change to payroll processing.
4. Educate employees
Communicate the on-demand pay program to your employees. Provide detailed information on how it works, the benefits, and how they can access their funds. Conduct training sessions or informational campaigns to ensure that employees are well-informed.
5. Evaluate the impact on company finances
Before and during implementation, evaluate how on-demand pay can influence the company finances. This includes either irregular payments or rapid micro-loans when wages are forwarded by an on-demand pay provider.
6. Track usage patterns
Analyze usage patterns to understand how often your employees are accessing on-demand pay. This information can help you make data-driven decisions about the program’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.