Shift Differential
What is a shift differential?
Shift differential is a premium rate offered to employees who work outside of the conventional work schedule, such as night shifts, weekends, or holidays. This additional compensation is not required under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), however, it is a common practice in businesses that operate around the clock, including sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and retail.
How does shift differential work?
As mentioned, shift differentials are extra pay added to employees’ hourly wages when they work less desirable shifts outside of normal daytime hours. Companies determine which shifts qualify for differential pay, such as evenings, overnights, weekends, and holidays.
This differential pay is usually a fixed extra amount per hour, such as an additional $1 or $2 per hour worked during this time. Alternatively, it can be calculated as a percentage, like 10% above base rate.
While offering shift differential pay is not mandatory by law, when an employer chooses to provide this benefit, it must comply with the applicable state and federal labor laws. This includes accurate tracking and calculation of hours worked, ensuring that the additional pay is properly reflected in the employee’s total compensation for the relevant pay periods.
The specific details of how shift differentials are implemented, including the rates and the shifts that qualify for such pay, can vary significantly between different employers and industries. This flexibility allows companies to tailor their compensation strategies to suit their operational needs and to attract and retain staff for these more challenging work hours.
Shift differential examples
Here are a few examples of how shift differentials might be structured in different industries or organizations:
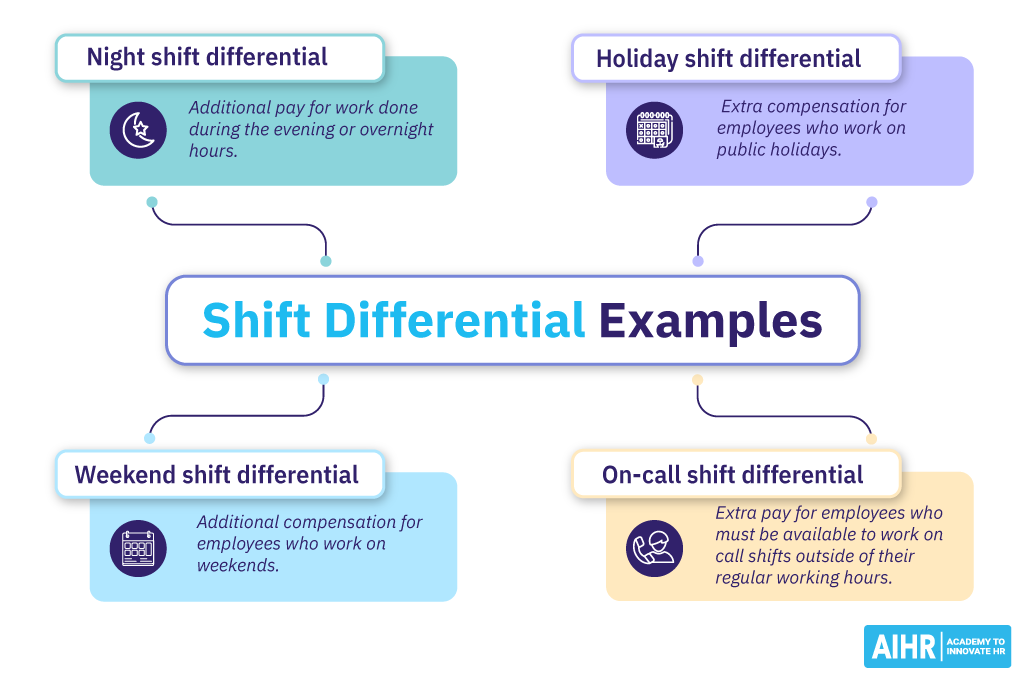
1. Night shift differential
Night shift differential pay is designed to provide fair compensation for work performed during typical sleeping hours. This additional pay benefits those in roles that demand overnight work, such as in security or healthcare sectors.
2. Holidays shift differential
Holiday shift differential is the additional pay employees receive for working on public holidays, such as Christmas, Thanksgiving, New Year’s Day, etc. An example is a bonus pay rate of an extra $4.00 per hour for employees working on federal holidays.
3. Weekend shift differential
Weekend shift differential refers to the extra pay given to employees who work during the weekend. For instance, an additional $2.50 per hour for a retail employee working on Saturdays and Sundays.
4. On-call shift differential
On-call shift differential is the extra pay provided to employees who are assigned on-call shifts outside of their normal working hours. This type of compensation is common in industries where workers may need to be called in at short notice, such as healthcare, IT, or emergency services.
Calculating shift differential
Calculating shift differential involves a straightforward process:
1. Identify the normal hourly wage.
2. Determine the shift differential rate (either a percentage of the hourly wage or a flat rate).
3. Multiply the number of hours worked during the differential period by the shift differential rate.
4. Add the result to the employee’s regular earnings for the shift.
Example 1:
An employee earns a standard rate of $15/hour. For a night shift, they receive a differential of 10%. If they work 8 hours, the calculation is as follows:
$15 x 10% = $1.50 (differential per hour)
$1.50 x 8 hours = $12
Total earnings for the shift = ($15 x 8 hours) + $12 = $132
Example 2:
An employee has a standard wage of $10/hour. The weekend shift differential is an additional $2 per hour. Working 10 hours across the weekend, the calculation is:
$2 x 10 hours = $2
Total earnings for the shift = ($10 x 10 hours) + $20 = $120
HR tip
Offering shift differentials can be highly advantageous for organizations looking to attract and retain talent, especially those with operations that span 24/7. By providing additional compensation for less desirable or inconvenient hours, organizations demonstrate a recognition of the extra effort required by these roles. This not only boosts morale but also positions the company as a more attractive employer, helping to draw in a wider pool of candidates.
HR best practices when developing a shift differential policy
Implementing shift differential policies can enhance staffing strategies for organizations with continuous operations. Here are some best practices for HR professionals:
1. Clear definition of shifts
Explain which hours and days qualify for the differential, such as weekends, holidays, evenings, overnight shifts etc.
2. Comprehensive eligibility criteria
Define who qualifies for shift differentials, including job function and level of responsibility. Apply the policy consistently across all eligible employees to prevent discrimination or favoritism.
3. Policy communication
Make the policy easily accessible, such as in the employee handbook or on the company intranet.
4. Integration with pay structure
Decide how much more employees working these shifts will earn. This could be a percentage increase over standard wages or a fixed amount.
5. Alternative compensation options
Consider offering non-monetary alternatives like extra paid time off, flexible scheduling or other perks as well as financial differentials.
6. Regular policy reviews
Regularly review and adjust the policy as needed. This could be due to changes in market conditions, labor laws, or company operations.
FAQ
Shift differential pay is typically not included in an employee’s base pay. Instead, it is an additional amount that is added to the base pay for the hours worked during specific shifts, like night shifts, weekends, or holidays.
Shift differential is not the same as overtime. Overtime typically refers to additional pay granted for hours worked beyond the standard 40-hour work week. Shift differential, on the other hand, is a premium paid for working non-standard hours, such as night, weekend, or holiday shifts, regardless of the total number of hours worked.
A shift differential rate is the additional compensation paid to an employee for working hours or shifts that are outside the normal business hours, such as evening, night, weekend, or holiday shifts. It is typically expressed as a percentage of the employee’s standard hourly rate or as a fixed additional amount per hour.