Organic Organizational Structure
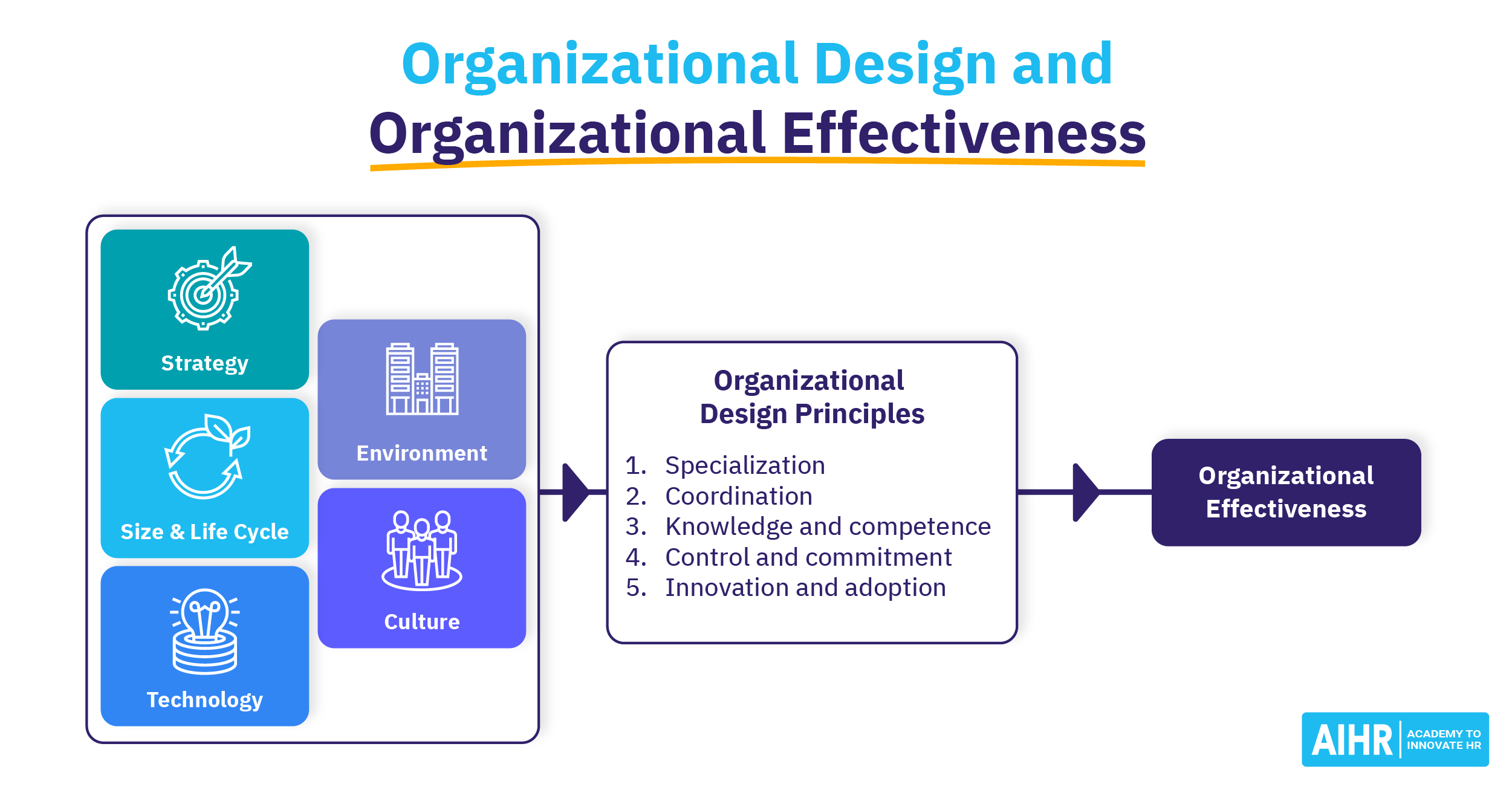
What is an organic organizational structure?
An organic organizational structure is a flexible, decentralized form of organization that emphasizes an adaptive, informal network approach to management and decision-making.
This type of structure allows for a more fluid and dynamic decision making process, often empowering lower-level employees and encouraging collaboration across departments and levels.
Key characteristics of an organic organizational structure
Some of the most significant characteristics of an organic organizational structure include:
- Low levels of formalization and standardization: There are fewer formal rules, procedures, and hierarchies.
- Decentralized decision-making: Authority and decision-making responsibilities are spread throughout the organization rather than being centralized at the top.
- Emphasis on teams and collaboration: Teams and individuals work across boundaries, strongly emphasizing collaboration and cooperation.
- Employee empowerment: Employees in an organic structure often have greater autonomy and are empowered to make decisions that affect their work.
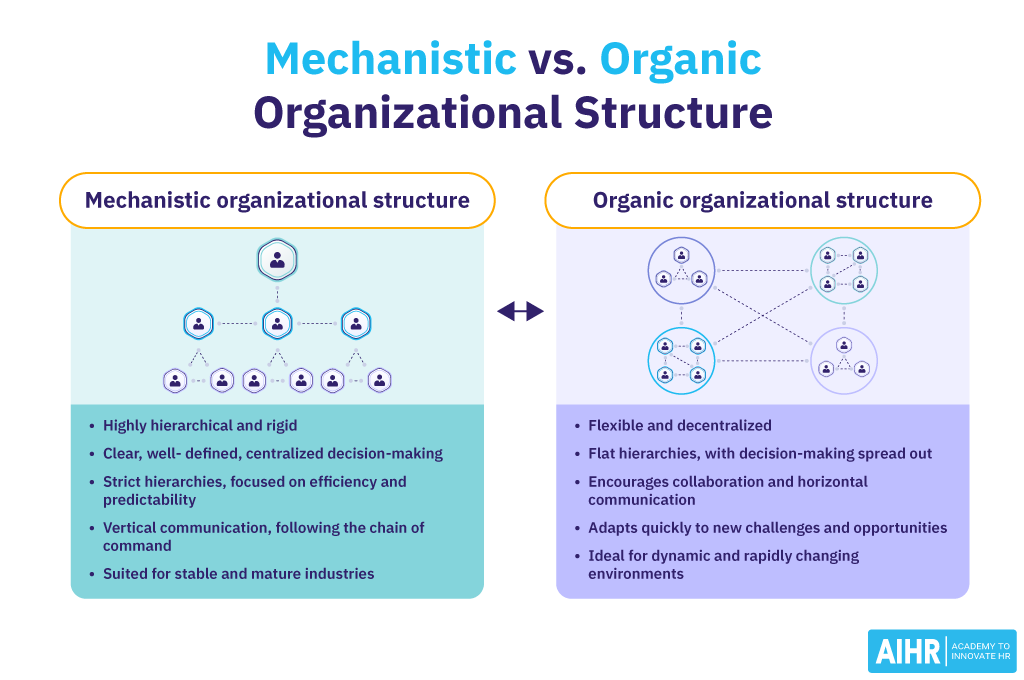
Mechanistic vs organic organizational structure
| Aspect | Mechanistic organization | Organic organization |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical, with clear, rigid departmental boundaries | Flat, with flexible and changing duties |
| Authority | Centralized decision-making | Decentralized decision-making |
| Communication | Vertical (top-down) | Lateral and horizontal, encouraging the flow of information |
| Decision-making | Made by top management, with little input from lower levels | Collaborative, with input from various levels of the organization |
| Innovation | Less emphasis on innovation, changes are slow and systematic | Encourages innovation and adaptability |
Organic organizational structure advantages
- Flexibility and adaptability: Organic structures allow the organization to quickly adapt to changes in the market, technology, customer preferences, or competitive landscapes.
- Creativity and innovation: The less formalized and more collaborative nature of organic structures fosters an environment where creativity and innovation are encouraged.
- Improved employee satisfaction: A more relaxed and informal work environment, combined with greater autonomy and the opportunity for personal growth, can lead to higher levels of job satisfaction.
- Employee development: The dynamic environment of an organic organization encourages continuous learning and development, as employees are exposed to a wider range of tasks and projects.
Organic organizational structure limitations
- Lack of clarity: The flexibility of organic structures can lead to a lack of clarity in roles and responsibilities. Employees may be unsure about their duties, decision-making authority, and whom to report to, potentially leading to inefficiencies.
- Difficulty in scaling: This structure might work well in small to medium-sized organizations but can become challenging to maintain as the organization grows due to informal communication and procedures becoming chaotic.
- Potential for conflict: Decentralized decision-making can increase the likelihood of conflict as different individuals or teams might pursue conflicting priorities without a clear hierarchy to resolve disputes, leading to tension and disagreements.
- Risk of overwork: The flexibility and emphasis on innovation can result in employees taking on too many responsibilities or working longer hours, especially if boundaries are not well-established.
Organic organizational structure examples
Companies with an organic organizational structure often operate in industries that are rapidly changing or that require a high degree of innovation and creativity. Here are examples of types of companies that often adopt an organic organizational structure:
- Technology startups: Many tech startups adopt organic structures to encourage innovation and adapt quickly to technological advancements and market changes.
- Research and development firms: Companies focused on R&D work in fields such as biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and engineering may use organic structures to promote knowledge sharing and innovation among scientists and researchers.
- Education and research institutions: Certain departments or initiatives within universities and research institutions might operate organically to foster interdisciplinary research and innovative teaching methods.
How to implement an organic organizational structure: Tips for HR
Here are several tips for HR professionals on how to effectively implement an organic organizational structure:
- Understand the basics of organic structure: Grasp the core principles of organic structure, focusing on flexibility, decentralized decision-making, and open communication to guide the transition.
- Evaluate company size and needs: Tailor the organic structure to the company’s specific size and requirements, considering how different departments and teams will interact within this framework.
- Develop a change management strategy: Create a detailed strategy that addresses communication, stakeholder engagement, and timelines, ensuring a structured approach to the transition.
- Train managers to be facilitators: Equip managers with the skills to support and empower their teams, emphasizing facilitation, collaboration, and decentralized decision-making.
- Plan the transition: Outline the steps, milestones, and goals of the transition, including mechanisms to address challenges and ensure alignment across the organization.
- Continuously evaluate and adapt: Set up feedback loops and performance metrics to regularly assess the effectiveness of the organic structure, making adjustments as needed.
FAQ
An example of an organic model of organization is a tech startup characterized by its flexible structure, decentralized decision-making, and open communication. In this environment, teams form dynamically to tackle projects, fostering innovation and rapid responses to market shifts. This model promotes a culture of collaboration and adaptability, essential for thriving in the fast-paced tech industry.
Organic organizations focus on flexibility, adaptability, and collaboration. They prioritize decentralized decision-making, open communication, and cross-functional teams to foster innovation and respond quickly to market changes.