Geographic Pay Differentials
What are geographic pay differentials?
Geographic pay differential refers to pay at a different rate for similar jobs based on the location. Geographic location, in this instance, refers to cities, states, countries, territories, etc. The premise of geographic pay differential is based on the cost of living, market rates, and various other factors. For example, living in a large city like New York will be different from living in a smaller city where living costs are lower.
Why are geographic pay differentials used?
There are various reasons why a geographic pay differential can be used:
- Different compensation rules: Some cities or countries have a different approach to fixed pay vs. variable pay. The tax structure might be different as well.
- Cost of living: Some geographies are more expensive to live in than others due to various factors. A geographic pay differential provides supplemental pay to adjust for the high cost of living in these locations.
- External factors: Inflation and unemployment are among the external factors that may influence the need for a geographic pay differential.
Recent changes to geographic pay differential practices
With the recent increase in remote work, geographic pay differential policies have come to the forefront. Some companies have chosen to implement a fixed “geo-differential” pay rate percentage, irrespective of the location.
Remote work has moved from being a perk to being the norm in many cases. Working remotely also has a monetary value (i.e., the savings of not traveling to the office or the increased associated costs of working from home).
For example, imagine an employee who previously worked at the company’s headquarters in a large metropolitan city who has now requested to move back home to a smaller, less expensive city. Because remote work is seen as a benefit in this instance, the employee’s salary may be reduced due to geographic pay differentials.
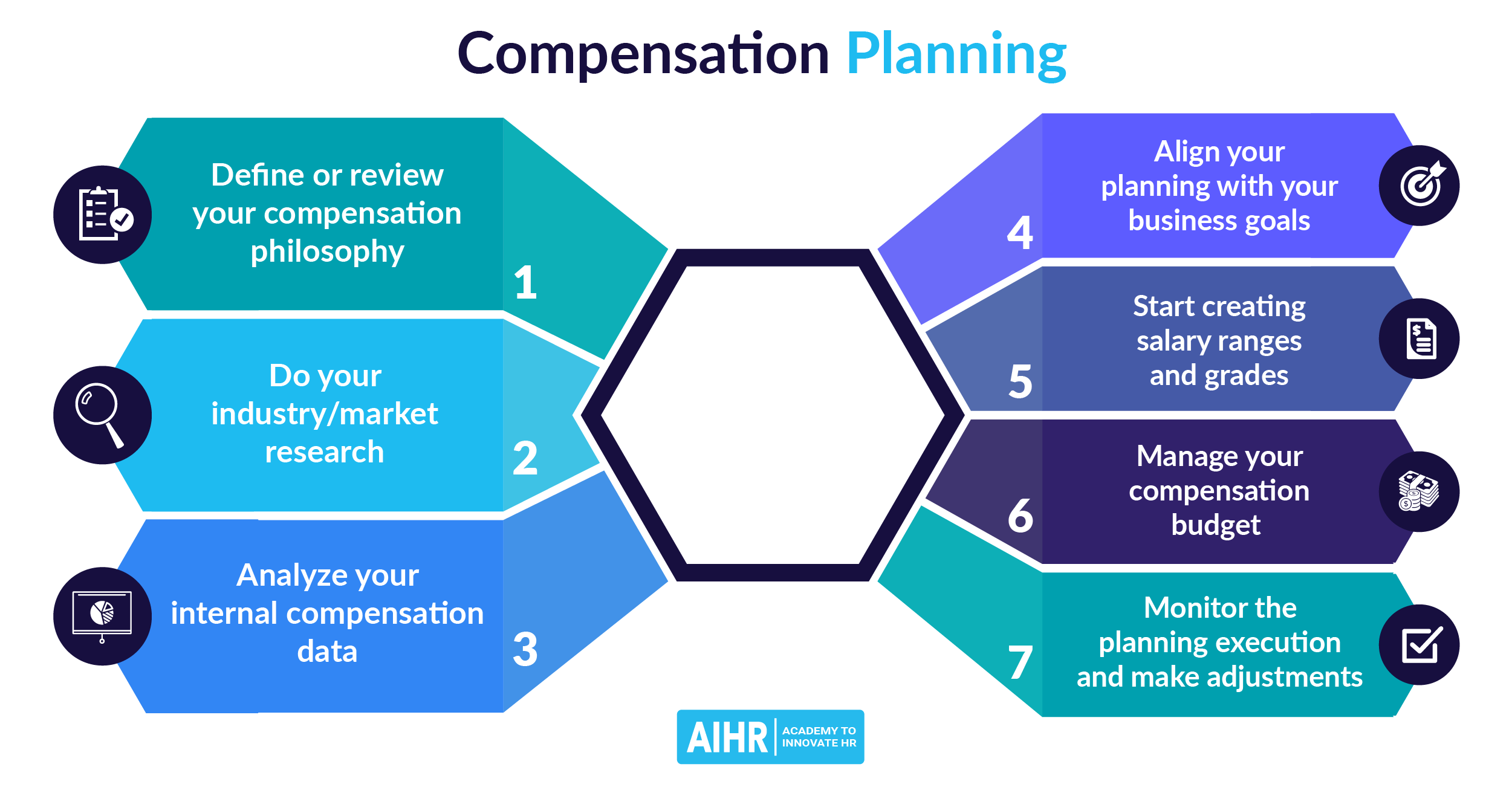
How to determine geographic pay differentials
To determine geographic pay differentials, there are two established methods:
- Accessing geographic pay data. Various pay consulting firms conduct salary surveys and gather data that can be used to estimate the pay levels and cost of living in a particular state, city, region, or country. This is usually represented as a percentage.
- Combining the cost of living and cost of labor data in a particular state, city, region, or country. This data is usually published by the government.
To calculate geographic pay differentials, you can use the below two methods:
1. Using percentages
Most companies have a base salary range. As an example, a company is advertising the position of a marketing executive, with a salary range of $50,000 to $130,000.
Candidate A lives in a more expensive city, whereas Candidate B lives in a less expensive city.
Using the data the company has collected on these geographies, a 15% premium is added to the position for Candidate A.
So, Candidate A was initially earning the minimum salary of $50,000, and the premium paid would be $7,500 ($50,000 x 15%). That would lead to a total of $57,500.
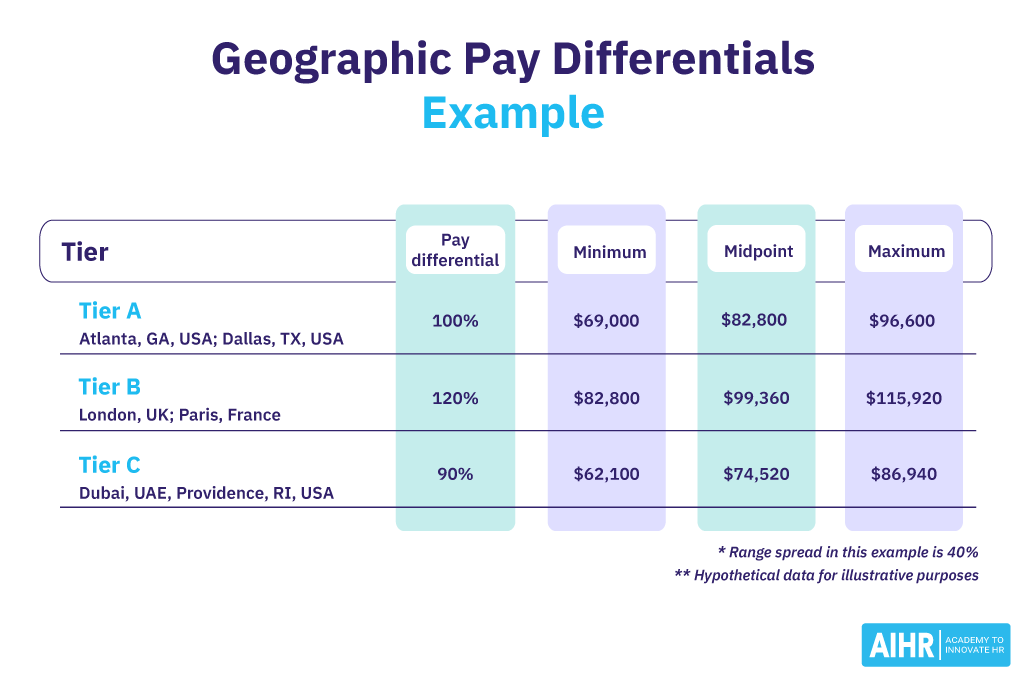
The result of calculating various geographic pay differentials could look something like this:
2. Using a fixed amount
Based on research, survey data, and input from internal sources, a company can allocate a fixed amount per position and geography. For example, a consulting company might associate a $5,000 premium for all consultants living in City A.