FLSA Status
What is FLSA status?
The Fair Labour Standards Act (FLSA) is the federal regulation for employee working hours and pay standards. It determines the exempt or non-exempt status of jobs and overtime requirements.
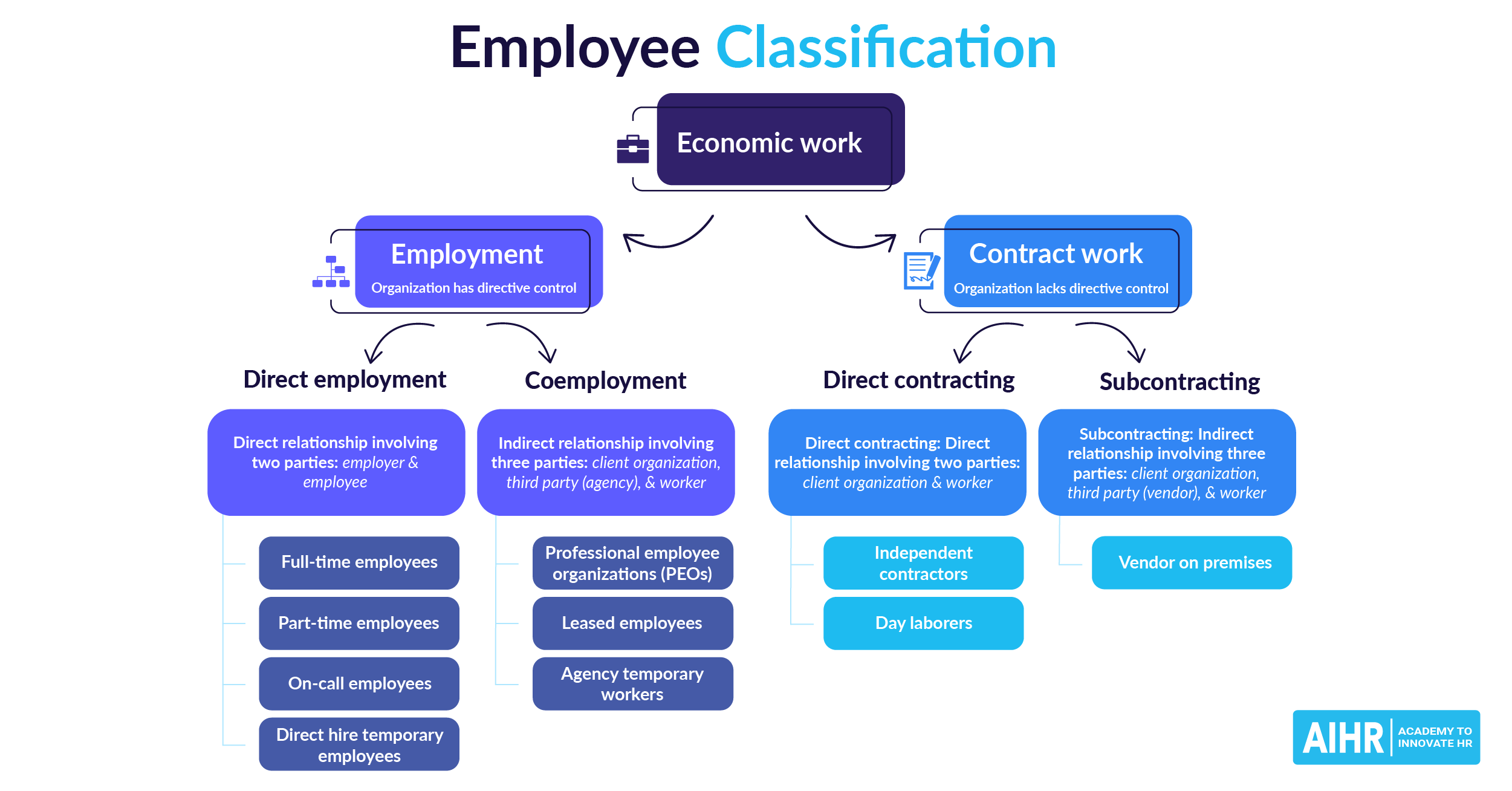
An employee’s FLSA status describes whether that employee is classified as exempt or non-exempt.
What is an exempt employee?
An exempt employee is not subject to FLSA overtime requirements. These workers typically receive an annual salary that doesn’t change based on the number of hours worked.
What is a non-exempt employee?
A non-exempt employee is entitled to compensation — at 1.5 times their regular pay — for the hours they work beyond the standard 40-hour workweek.
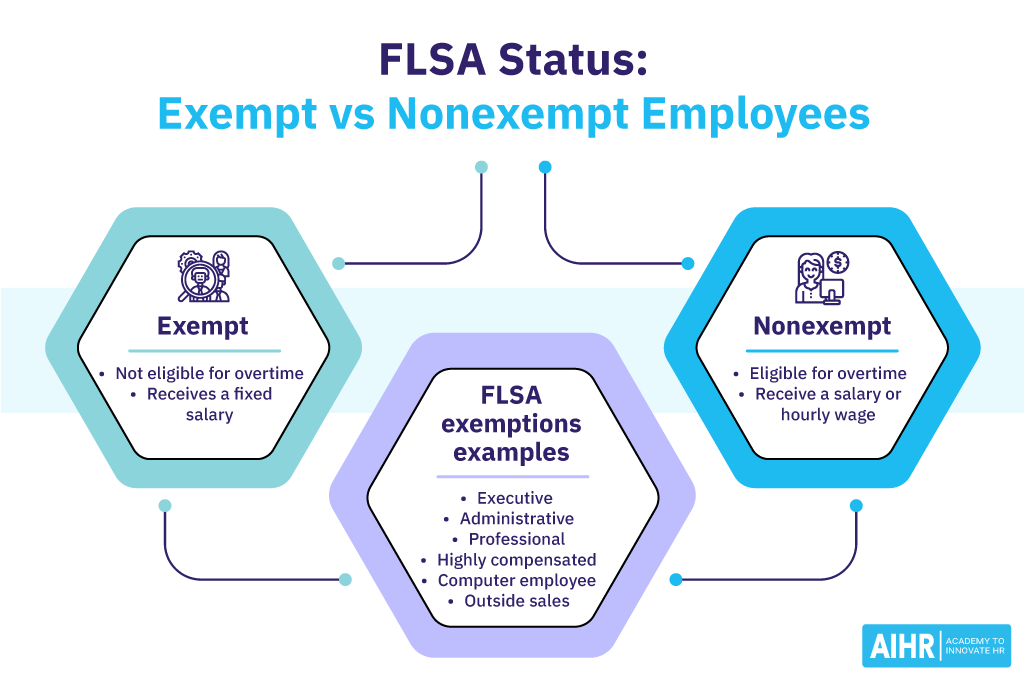
FLSA exemptions
In most cases, the determining factor for classifying an employee as exempt or non-exempt is the nature of the duties performed.
Here are some of the positions that commonly fall under exempt status because of their job duties.
- Executive
- Administrative
- Professional
- Highly compensated
- Computer employee
- Outside sales
FLSA status determination
An employee must meet the following criteria to be considered exempt, i.e., not subject to FLSA overtime requirements:
- Earn no less than $684 a week, which comes to $35,658 per year (salary level test).
- Be compensated on a salary basis (salary basis test).
- Perform exempt job duties (duties test).
Let’s take an in-depth look at each of these criteria.
- Salary level test. Workers earning below the FLSA threshold of $684 per week ($35,568 per year) are considered non-exempt — and vice versa. Employers may use incentive payments and nondiscretionary bonuses towards that total, but only up to 10% of the salary requirement.
- Salary basis test. Rather than earning an hourly wage, salaried employees are guaranteed a fixed, predetermined amount of money. Their pay doesn’t change regardless of variations in their work schedule in a given week. Their FLSA status can be classified as exempt.
- Duties test. Job duties also come into play when determining FLSA status. The FLSA considers certain positions exempt due to the nature of their job duties. These special FLSA exemptions include executives, administrators, and other roles requiring specific skills or education.
HR tip
For an employee to be FLSA exempt, they must pass the salary level test and salary basis test and perform exempt job duties.
How HR can remain compliant with FLSA
As an HR professional, it’s imperative you understand what it takes to stay compliant with FLSA and its provisions. Here are some key considerations to keep your company compliant when determining FLSA status.
- Conduct a job audit. Audit the roles at your company to understand which are exempt and non-exempt. Take a deep dive into the required tasks, work hours, title, and skill level for each position.
- Minimum wage. What’s the highest regulated minimum wage for your company’s line of work? The federal requirement for minimum wage at $7.25 per hour. Check the minimum wage requirement in your state, as it may vary.
- Overtime. If an employee works over 40 hours in one week, you must compensate them for the extra hours. This rule applies even if there are restrictions on the number of hours employees can work each week.
- Hours worked. Outline the standard hours worked for the organization and what happens if a worker does not stick to the rules. It’ll go a long way toward ensuring employees don’t accumulate unwanted overtime hours.
- Record-keeping. Maintaining accurate and up-to-date records is key to staying compliant with FLSA. Proper documentation will help ensure your company pays employees accordingly based on FLSA status.