Fixed Pay
What is fixed pay?
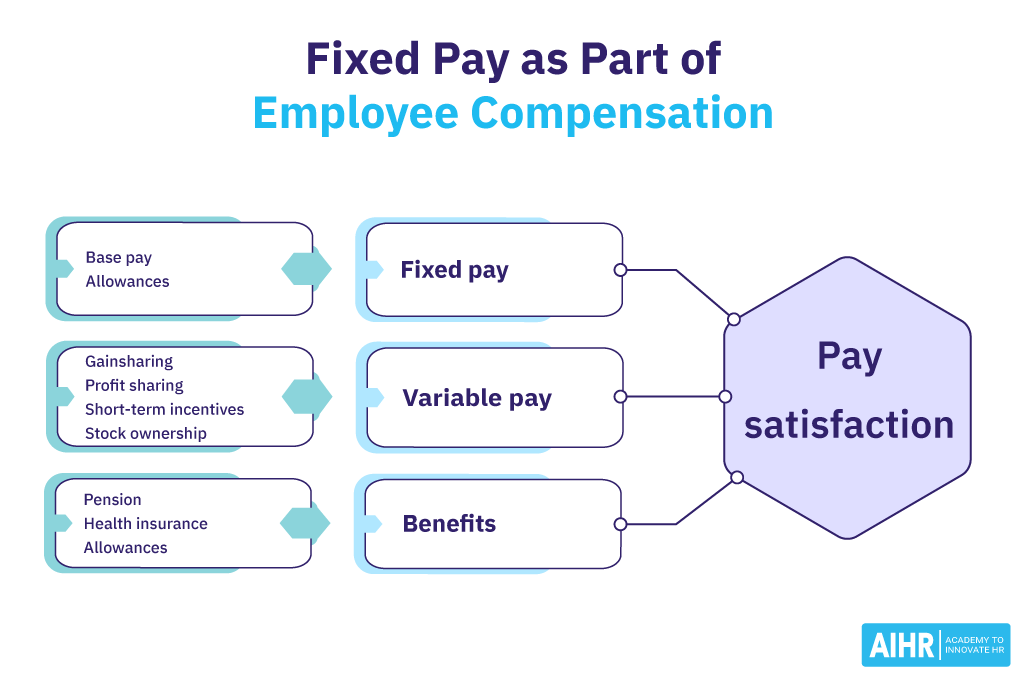
Fixed pay, or fixed salary, is the predefined and fixed amount paid to an employee by the employer at the end of every payroll cycle. Fixed pay includes all remuneration guaranteed by the company, most commonly in the form of a monthly or annual salary.
Additional contributions to things like medical insurance, a retirement fund, or allowances (car, house, etc.) may or may not be included in fixed pay, depending on the company policy and/or employment agreement.
The term ‘fixed’ indicates the same amount is paid to an employee on a regular basis, irrespective of hours worked or the quality of work performed.
Fixed pay vs. variable pay
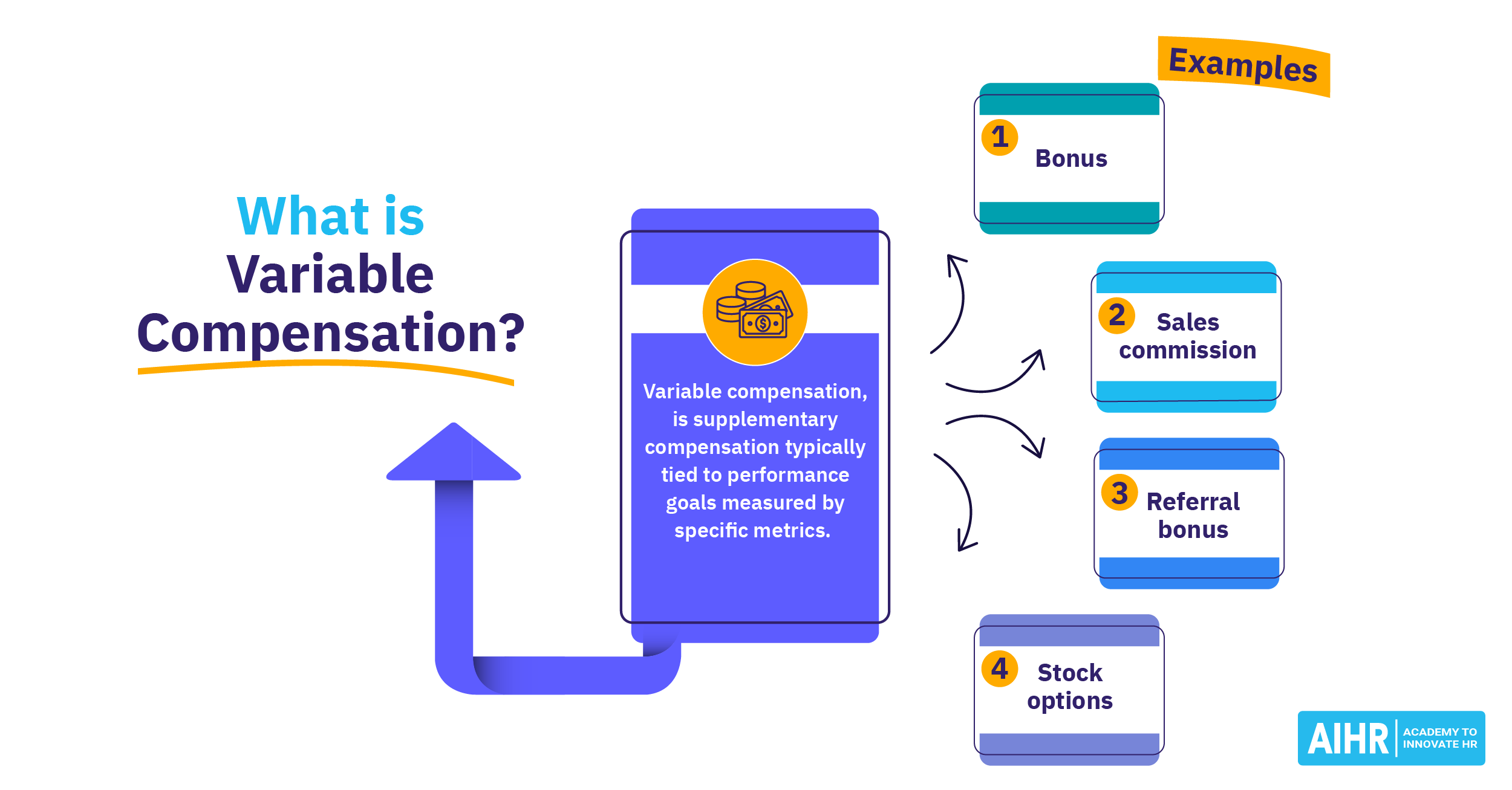
Variable pay is remuneration determined by employee performance. It is offered in addition to the employee’s fixed pay. Performance bonuses, sales commissions, referral bonuses, and profit-sharing are some examples of variable pay.
The term ‘variable’ indicates that the amount paid to an employee can change depending on the employee or company’s performance.
Example 1:
A manager is paid a salary of $2,000 every month. Included in the manager’s contract is a fixed housing allowance of $200 per month. These two regular payments comprise the fixed pay.
At the end of the year, the manager is paid a $4,500 bonus. The bonus is considered variable pay.
Example 2:
The same manager moves to a new city and has asked to work reduced hours. As a result, the company decides to switch the manager to earning an hourly wage.
The manager logs 32 hours in one month and 45 hours in the following month. The manager is also awarded a two-month allowance to help relocate to a new city. In addition, the manager is paid a sales commission of $450 for closing key deals for the company. All components of his pay, in this case, are considered variable pay.
Advantages and disadvantages of fixed pay
Advantages of fixed pay
- Budgeting: An organization can forecast and budget better, as there is not much change on a month-to-month basis in employees’ fixed salaries. It also allows employees to manage their finances better every month, as they know the amount in advance.
- Employee security: Some employees prefer to have the security of a fixed amount per month. It can have a positive effect on employee retention and satisfaction rates.
- Flexible working: In many instances, a fixed pay allows employees to have more flexible working hours. An employee can work a bit earlier or later and still be paid the same amount.
Disadvantages of base pay
- Performance: Fixed pay is not directly tied to performance, whereas variable pay is paid to employees for satisfactory or excellent performance. As a result, fixed pay may not encourage employees to go the extra mile.
- Less flexibility for the company: With fixed pay, an employer has to pay the same amount for an employee irrespective of the amount of work available. On the other hand, variable pay allows the company to manage costs by managing shifts due to an increasing or decreasing workflow.